An experimental demonstration of the effect of group size on cultural accumulation
Abstract
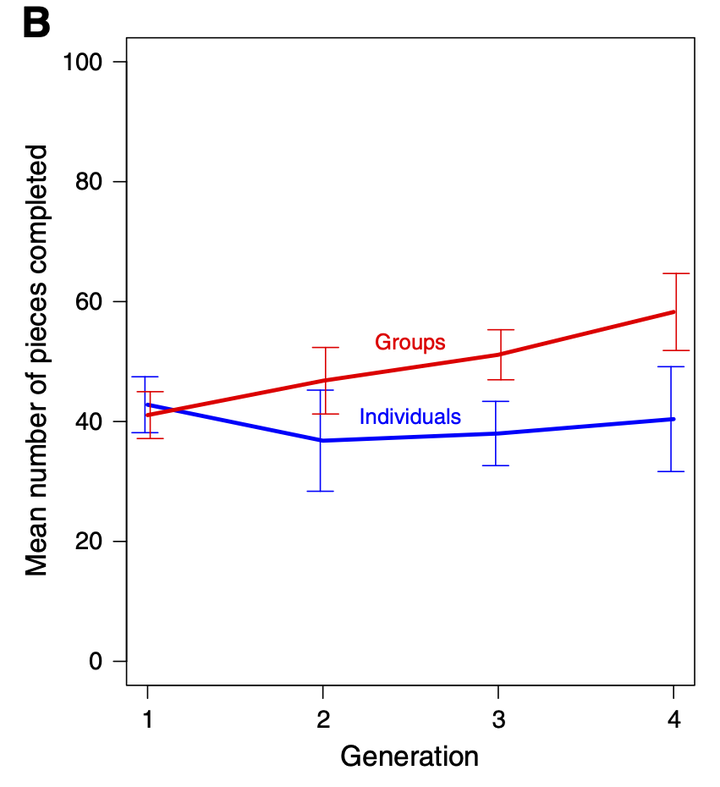
Cumulative culture is thought to have played a major role in hominin evolution, and so an understanding of the factors that affect cultural accumulation is important for understanding human evolution. Population size may be one such factor, with larger populations thought to be able to support more complex cultural traits. This hypothesis has been suggested by mathematical models and empirical studies of small-scale societies. However, to date there have been few experimental demonstrations of an effect of population size on cultural accumulation. Here we provide such a demonstration using a novel task, solving jigsaw puzzles. 80 participants divided into ten transmission chains solved puzzles in one of two conditions: one in which participants had access to one semi-completed puzzle from the previous generation, and the other in which participants simultaneously saw three semi-completed puzzles from the previous generation. As predicted, the mean number of pieces solved increased over time in the three-puzzle-per-generation condition, but not in the one-puzzle-per-generation condition. Thus, our experiment provides support for a hypothesized relationship between population size and cultural accumulation. In particular, our results suggest that the ability to simultaneously learn from multiple cultural models, and combine the knowledge of those multiple models, is most likely to allow larger groups to support more complex culture.